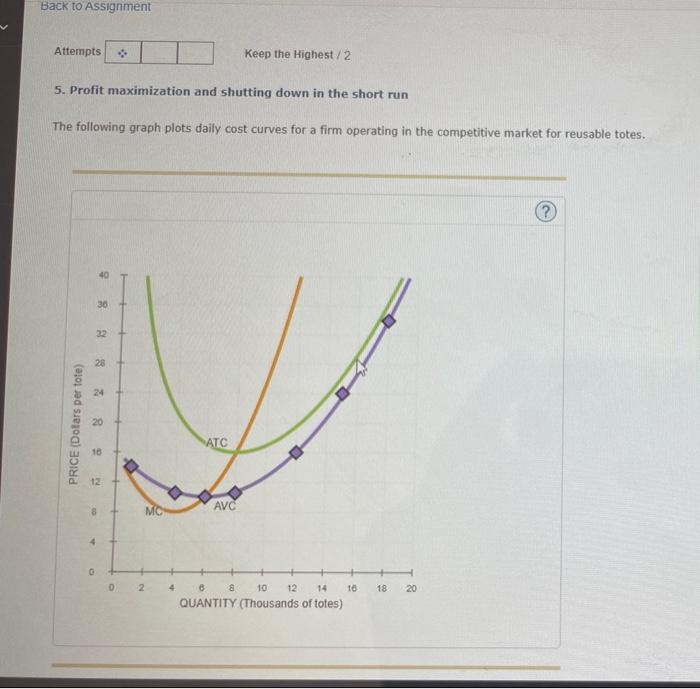
5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. PRICE (Dollars per sweater) 0 + 0 + 2 + + + 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 QUANTITY (Thousands of sweaters) 18 20 For each price in the following table,
14. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run.docx – 14. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run The following graph plots | Course Hero
Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from Table 1. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at Q = 60, TR = 240 and TC = 165. The difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. The firm doesn’t make a profit at every level of output.

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
Maximizing Profit or Minimizing Loss in the Short Run. Recall that the short run is a period too brief to allow firms to enter or leave the market. The demand and cost conditions shown in panel (a) of Exhibit 10 indicate that this firm earns economic profit in the short run. At the firm’s profit-maximizing quantity, average total cost, c, is

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Solved Profit maximization and shutting down in the short | Chegg.com
Figure 1. The Shutdown Point for the Raspberry Farm. In panel (a), the farm produces where MR = MC at Q = 65. It is making losses of $47.50, but price is above average variable cost, so it continues to operate. In panel (b), demand has fallen so that price ($1.50) is less than average variable cost ($1.72).
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
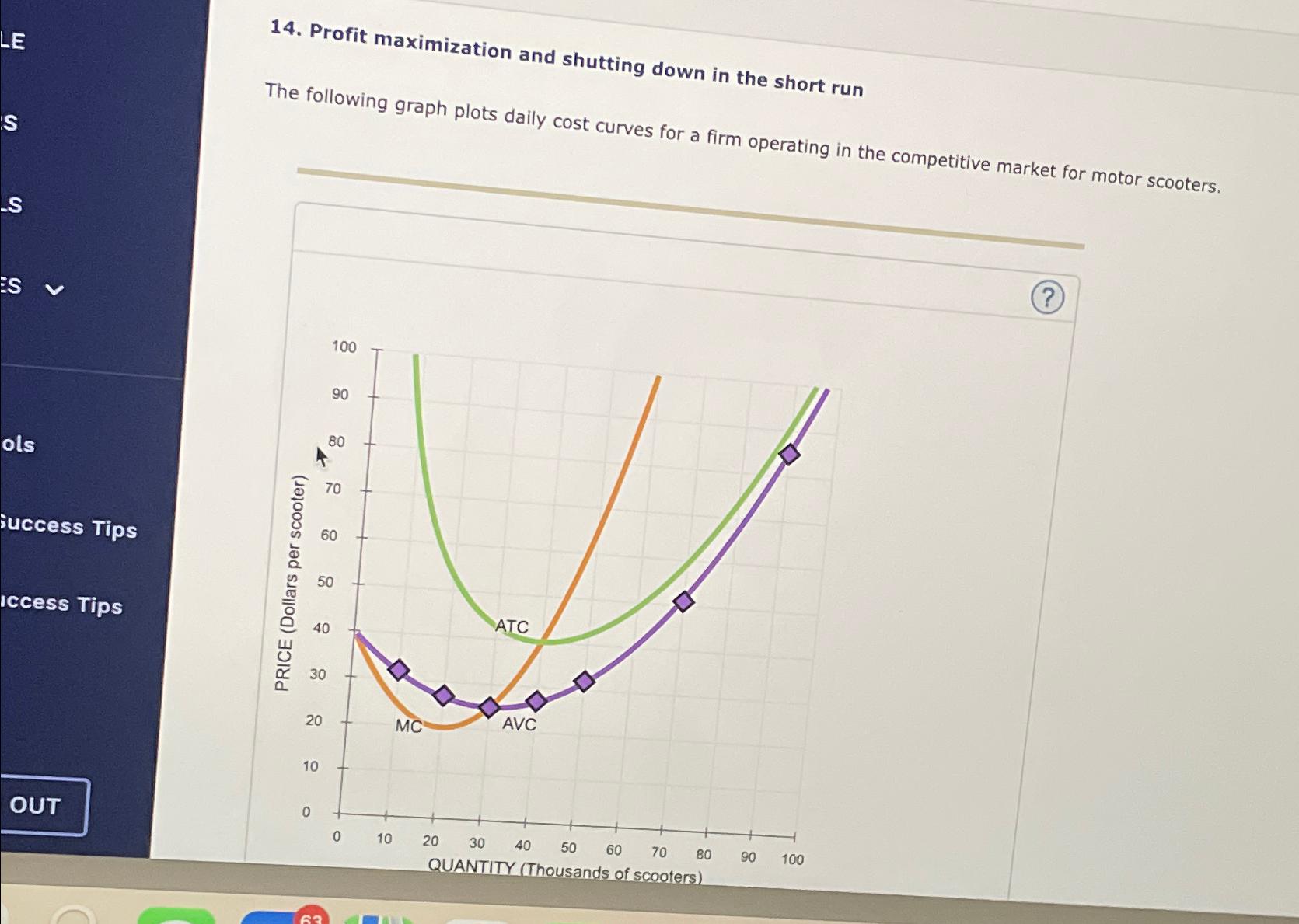
5. Profit Maximization And Shutting Down In The Short Run
Figure 1. The Shutdown Point for the Raspberry Farm. In panel (a), the farm produces where MR = MC at Q = 65. It is making losses of $47.50, but price is above average variable cost, so it continues to operate. In panel (b), demand has fallen so that price ($1.50) is less than average variable cost ($1.72).
Maximization of short-run profits. The average and marginal cost curves just deduced are the keys to the solution of the second-level problem, the determination of the most profitable level of output to produce in a given plant. The only additional datum needed is the price of the product, say p 0.. The most profitable amount of output may be found by using these data.
Solved 5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short | Chegg.com
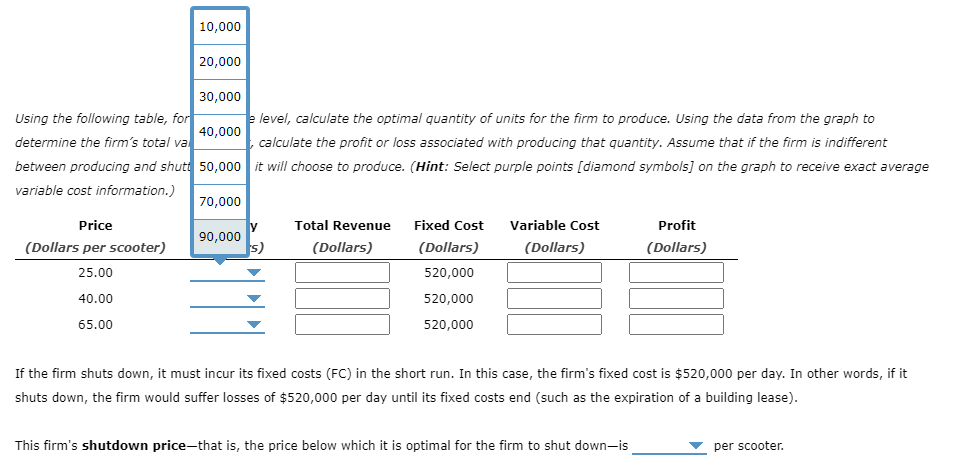
Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run The following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for porch swings. Using the following table, for each arice level, calculate the optimal quantity of units for the firm to produce.
Solved 5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short | Chegg.com
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Profit Maximization and Shut Down Point – YouTube
Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run The following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for porch swings. Using the following table, for each arice level, calculate the optimal quantity of units for the firm to produce.

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
14. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run.docx – 14. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run The following graph plots | Course Hero
5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. PRICE (Dollars per sweater) 0 + 0 + 2 + + + 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 QUANTITY (Thousands of sweaters) 18 20 For each price in the following table,

Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
Solved Profit maximization and shutting down in the short | Chegg.com
Maximizing Profit or Minimizing Loss in the Short Run. Recall that the short run is a period too brief to allow firms to enter or leave the market. The demand and cost conditions shown in panel (a) of Exhibit 10 indicate that this firm earns economic profit in the short run. At the firm’s profit-maximizing quantity, average total cost, c, is
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
A Founder’s Exponential Toolset: Wright’s Law, Moore’s Law, & More
A firm shut’s down temporarily when it can’t cover its variable cost, but it exits the industry for good when it’s economic profits are negative. In this video, learn more about how to use a graph of cost curves to determine when a firm shuts down, enters an industry, or exits an industry. Questions. Tips & Thanks.

Source Image: nfx.com
Download Image
Economics: Short run profit Maximisation in perfect competition:
Figure 1. The Shutdown Point for the Raspberry Farm. In panel (a), the farm produces where MR = MC at Q = 65. It is making losses of $47.50, but price is above average variable cost, so it continues to operate. In panel (b), demand has fallen so that price ($1.50) is less than average variable cost ($1.72).
Source Image: economicsmicro.blogspot.com
Download Image
PPT – Profit Maximization PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:3054903
Maximization of short-run profits. The average and marginal cost curves just deduced are the keys to the solution of the second-level problem, the determination of the most profitable level of output to produce in a given plant. The only additional datum needed is the price of the product, say p 0.. The most profitable amount of output may be found by using these data.

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
Profit Maximization and Shut Down Point – YouTube
PPT – Profit Maximization PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:3054903
Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from Table 1. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at Q = 60, TR = 240 and TC = 165. The difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. The firm doesn’t make a profit at every level of output.
Solved Profit maximization and shutting down in the short | Chegg.com Economics: Short run profit Maximisation in perfect competition:
A firm shut’s down temporarily when it can’t cover its variable cost, but it exits the industry for good when it’s economic profits are negative. In this video, learn more about how to use a graph of cost curves to determine when a firm shuts down, enters an industry, or exits an industry. Questions. Tips & Thanks.